NDT Synopsis (UT)
The Presented study covers an overview of the techniques which are used or could be used for onsite condition monitoring and effective NDT of different field & taking into account the complicated structure of the Product as well as possibility to make non-destructive testing in harsh on-site conditions.
Most inspectors have switched from conventional Destructive Testing technology to the more accurate and precise Non-Destructive system because of time savings.
NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) refers to an array of inspection techniques that allow inspectors to collect data about a materials or products without damaging it. NDT methods rely upon use of electromagnetic radiation, sound and other signal conversions to examine a wide variety of articles (metallic and non-metallic, artifacts and antiquities, infrastructure) for integrity, composition, or condition with no alteration of the article undergoing examination.
Here are the top reasons NDT is used by so many companies throughout the world.
Savings – Safety – Efficiency – Accuracy
A wide variety of NDT methods plays major roles in testing of Different Material. Therefore, choosing the right method and technique is an important part of the performance of NDT.
Here are the some most used NDT techniques:
Primary or Screening:
Visual NDT (VT)- Most basic and common inspection method, Visual Testing involves the collection of visual information on a material’s status. Very fast & low-cost inspection
Infrared & Thermal NDT (IR) -Thermography is a technique of obtaining an image of the heat distribution over the surface of an object.
Secondary NDT Techniques or Deep Analysis:
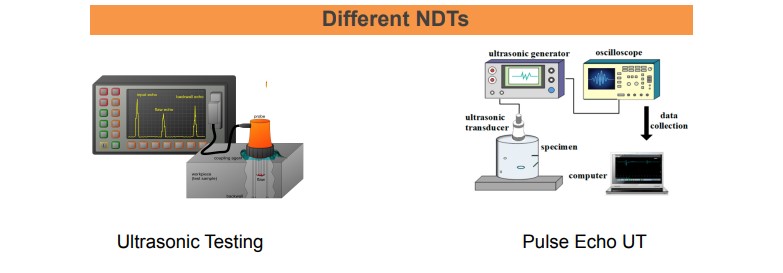
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): UT waves transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials.
Pulse Echo UT: The pulse-echo ultrasonic technique, ultrasound wave is excited and detected by two identical piezoelectric transducers (transmitter and receiver), which are glued to polished opposite sides of a sample.
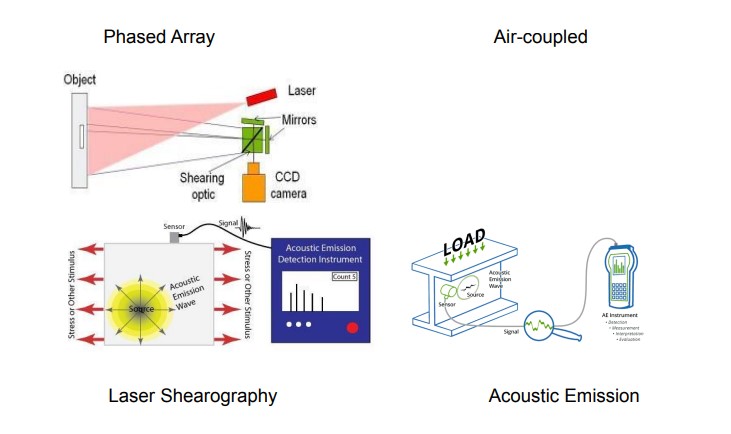
Phase Array UT: Phased Array is an ultrasonic testing technique that uses specialized multi-element “array” transducers and pulses those elements separately in a patterned sequence called “phasing”.
Air Coupled UT: Air Coupled UT use a transducer which generates sound waves in the ultrasonic range, above 18 kHz, by turning electrical energy into sound,
Laser Shearography: Shearography or Speckle pattern shearing interferometry is a measuring and testing method similar to holographic interferometry.
Acoustic Emission: Acoustic Emission (AE) is the class of phenomena whereby an elastic wave, in the range of ultrasound usually between 20 KHz and 1 MHz, is generated by the rapid release of energy from the source within a material. The elastic wave propagates through the solid to the surface.